Have you been told to learn to live with it?
At Advanced Healing Therapies we treat arthritic joints! Arthritis is a common condition that causes pain and inflammation in a joint. In the UK, around 10 million people have arthritis. It affects people of all ages, including children...
Types of arthritis
The two most common types of arthritis are:
osteoarthritis
rheumatoid arthritis
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis in the UK, affecting around 8 million people.
It most often develops in adults who are in their late 40s or older. It’s also more common in women and people with a family history of the condition. However, it can occur at any age as a result of an injury or be associated with other joint-related conditions, such as gout or rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis initially affects the smooth cartilage lining of the joint. This makes movement more difficult than usual, leading to pain and stiffness. Once the cartilage lining starts to roughen and thin out, the tendons and ligaments have to work harder. This can cause swelling and the formation of bony spurs, called osteophytes.
Severe loss of cartilage can lead to bone rubbing on bone, altering the shape of the joint and forcing the bones out of their normal position.
The most commonly affected joints are those in the:
hands
spine
knees
hips
Rheumatoid arthritis
In the UK, rheumatoid arthritis affects more than 400,000 people. It often starts when a person is between 40 and 50 years old. Women are three times more likely to be affected than men. Rheumatoid and osteoarthritis are two different conditions. Rheumatoid arthritis occurs when the body’s immune system targets affected joints, which leads to pain and swelling. The outer covering (synovium) of the joint is the first place affected. This can then spread across the joint, leading to further swelling and a change in the joint’s shape. This may cause the bone and cartilage to break down. People with rheumatoid arthritis can also develop problems with other tissues and organs in their body.
Other types of arthritis and related conditions
Ankylosing spondylitis – a long-term inflammatory condition that mainly affects the bones, muscles and ligaments of the spine, leading to stiffness and joints fusing together. Other problems can include the swelling of tendons, eyes and large joints.
Cervical spondylosis – also known as degenerative osteoarthritis, cervical spondylitis affects the joints and bones in the neck, which can lead to pain and stiffness.
Fibromyalgia – causes pain in the body’s muscles, ligaments and tendons.
Lupus – an autoimmune condition that can affect many different organs and the body’s tissues.
Gout – a type of arthritis caused by too much uric acid in the body. This can be left in joints (usually affecting the big toe) but can develop in any joint. It causes intense pain, redness and swelling.
Psoriatic arthritis – an inflammatory joint condition that can affect people with psoriasis.
Enteropathic arthritis – a form of chronic, inflammatory arthritis associated with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), the two best-known types being ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. About one in five people with Crohn’s or ulcerative colitis will develop enteropathic arthritis. The most common areas affected by inflammation are the peripheral (limb) joints and the spine.
Reactive arthritis – this can cause inflammation of the joints, eyes and urethra (the tube that urine passes through). It develops shortly after an infection of the bowel, genital tract or, less frequently, after a throat infection.
Secondary arthritis – a type of arthritis that can develop after a joint injury and sometimes occurs many years afterwards.
Polymyalgia rheumatica – a condition that almost always affects people over 50 years of age, where the immune system causes muscle pain and stiffness, usually across the shoulders and tops of the legs. It can also cause joint inflammation.
Symptoms of arthritis
The symptoms of arthritis you experience will vary depending on the type you have.
This is why it’s important to have an accurate diagnosis if you have:
joint pain, tenderness and stiffness
inflammation in and around the joints
restricted movement of the joints
warm, red skin over the affected joint
weakness and muscle wasting
Treating arthritis
There’s no cure for arthritis, but there are many treatments that can help slow down the condition.
For osteoarthritis, medications are often prescribed, including:
painkillers
non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
corticosteroids
In severe cases, the following surgical procedures may be recommended:
arthroplasty (joint replacement)
arthrodesis (joint fusion)
osteotomy (where a bone is cut and re-aligned)
Read more here; http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Arthritis/Pages/Introduction.aspx
Treatment for Arthritis at Advanced Healing Therapies
Using our reward winning technology we can;
Reduce the inflammation
Activate the lymph for detoxification
Encourage blood flow and circulation
Lift and tone muscles for easier movement
Help relaxation
Reduced the stress
Alleviate the pain
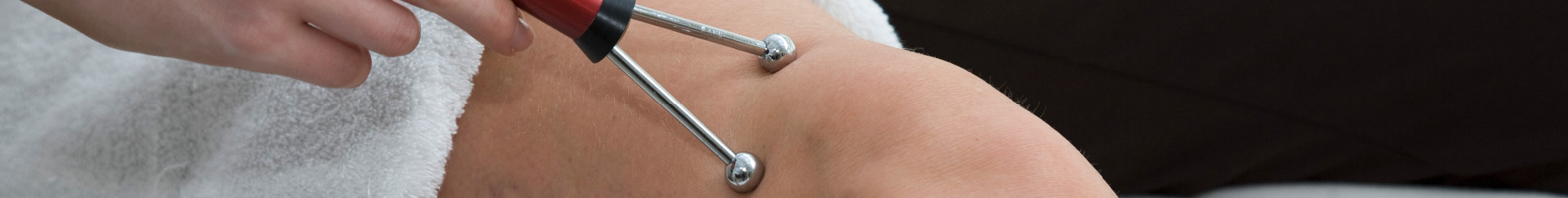
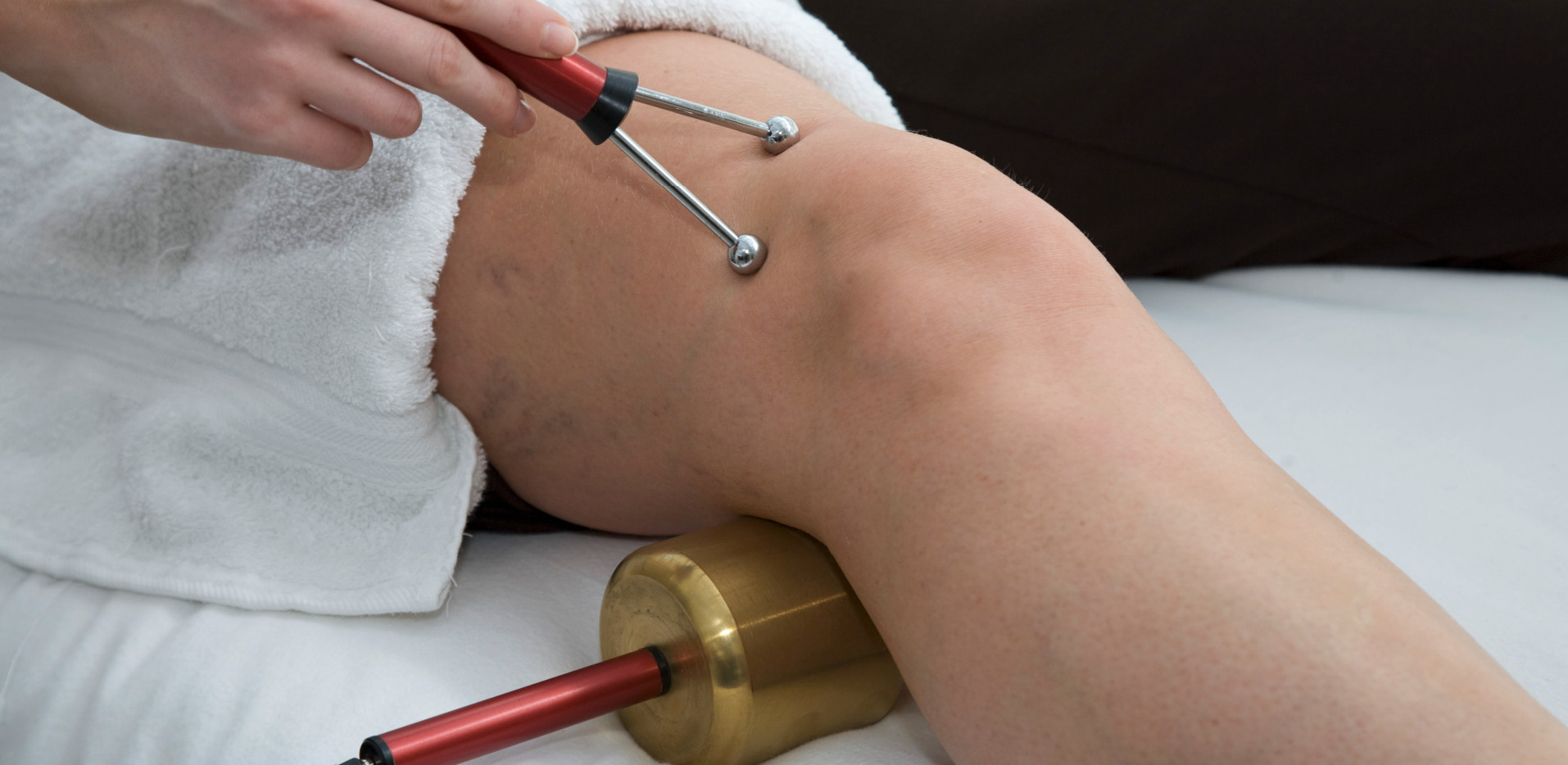
Electro-Myopulse Explanation
The Electro-Myopulse 75 was specifically designed to provide today’s clinician with an expedient method for treatment of a wide variety of muscle and connective tissue problems. The applications include:
Prevention or retardation of tissue atrophy
Relaxation of muscle spasm
Increasing local blood circulation
Muscle reeducation
Immediate post-surgical stimulation to prevent venous thrombosis
Maintaining or increasing range of motion
To accomplish this, the micro-current output waveforms were optimized to reflect changes in neuron muscle activity. This means the clinician has a expanded capability to assist the healing of the patient in a greater range of acute injury and chronic problems.
Share this post: